Proposed mechanism for the roles of ONOO – and U NO on PGHS-1 activity.
Download scientific diagram | Proposed mechanism for the roles of ONOO – and U NO on PGHS-1 activity. Peroxynitrite-derived radicals inactivate PGHS-1. In parallel, U NO 2 causes both from publication: Interactions between nitric oxide and peroxynitrite during prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-1 catalysis: A free radical mechanism of inactivation | Peroxynitrite (ONOO(-)) can serve either as a peroxide substrate or as an inactivator of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-1 (PGHS-1). Herein, the mechanism of PGHS-1 inactivation by ONOO(-) and the modulatory role that nitric oxide (*NO) plays in this process were | Free Radicals, Nitric Oxide and Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthases | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Prostaglandin Synthesis - an overview

Proposed mechanism for the roles of ONOO – and U NO on PGHS-1 activity.

Cardiovascular Consequences When Nitric Oxide and Lipid Signaling Converge

Crosstalk of mitochondria with NADPH oxidase via reactive oxygen and nitrogen species signalling and its role for vascular function - Daiber - 2017 - British Journal of Pharmacology - Wiley Online Library

Cardiovascular Consequences When Nitric Oxide and Lipid Signaling Converge
Peroxynitrite detoxification and its biologic implications - Document - Gale Academic OneFile

Proposed mechanism for the roles of ONOO – and U NO on PGHS-1 activity.

Prostaglandin H - an overview
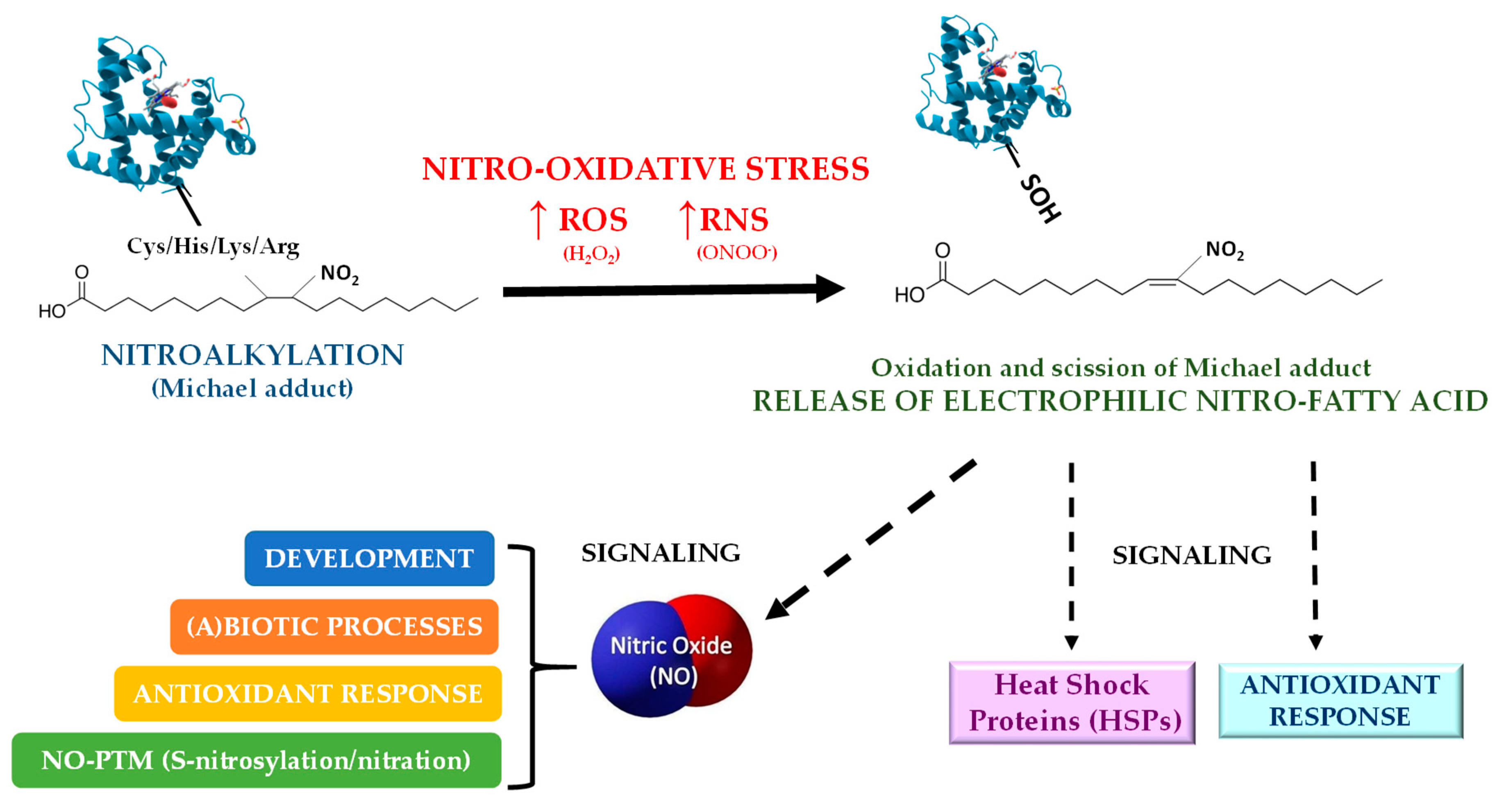
Plants, Free Full-Text

Heme catalyzes tyrosine 385 nitration and inactivation of prostaglandin H2 synthase-1 by peroxynitrite - Journal of Lipid Research

Prostaglandin H - an overview

How Can We Cure NO/ONOO− Cycle Diseases? A Review

Proposed mechanism for the roles of ONOO – and U NO on PGHS-1 activity.

Convergence of nitric oxide and lipid signaling: anti-inflammatory nitro-fatty acids. - Abstract - Europe PMC