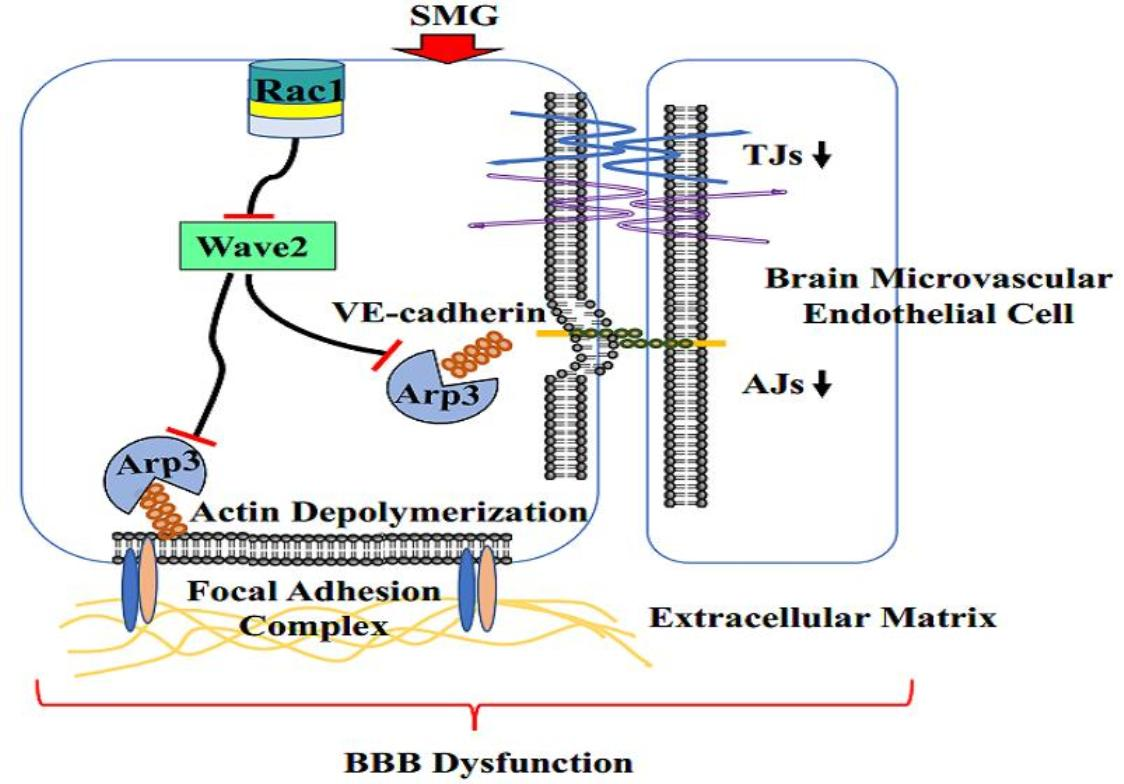
Dynactin-Dependent, Dynein-Driven Vesicle Transport in the Absence

HEATR5B associates with dynein‐dynactin and promotes motility of AP1‐bound endosomal membranes
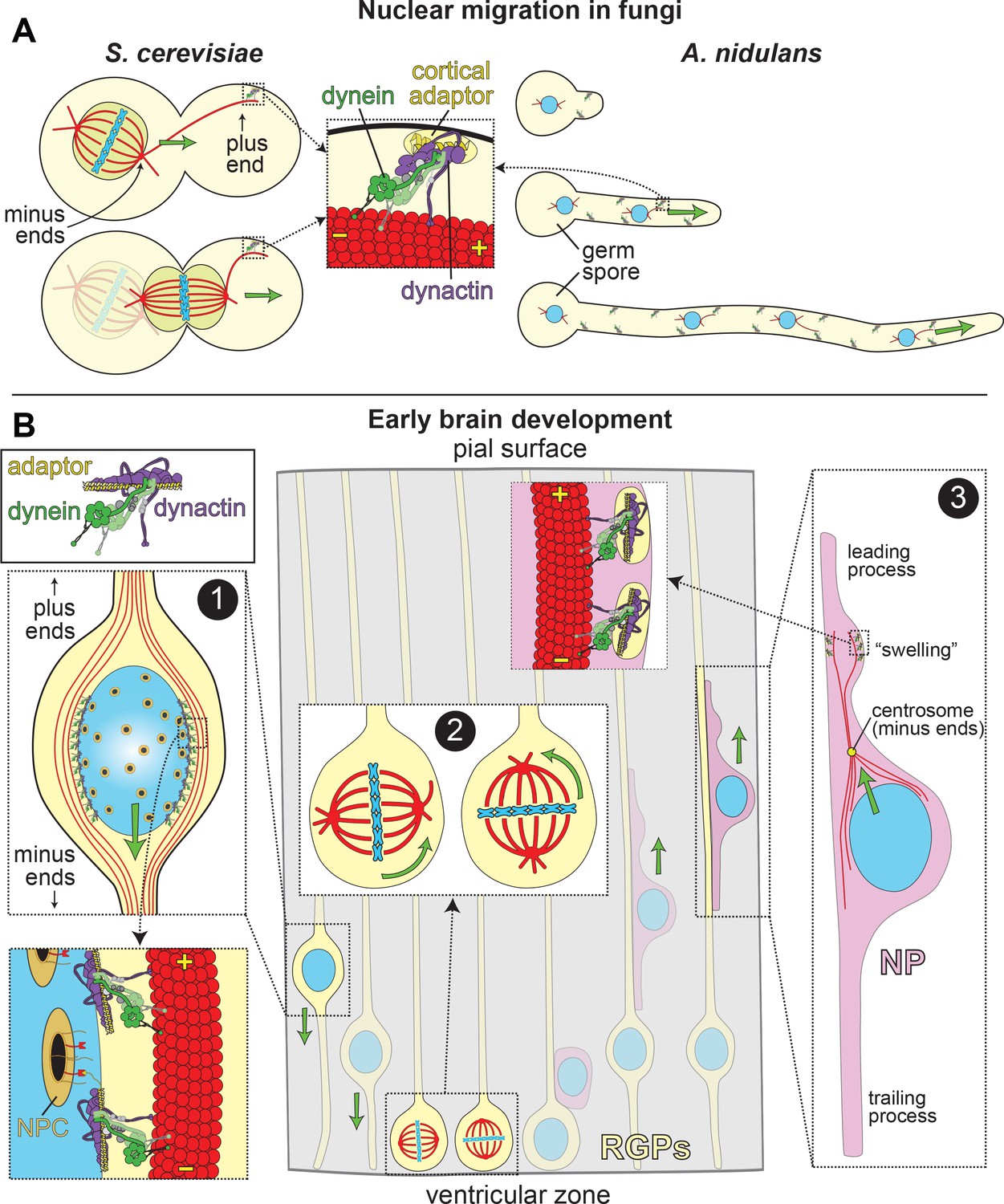
New insights into the mechanism of dynein motor regulation by lissencephaly-1
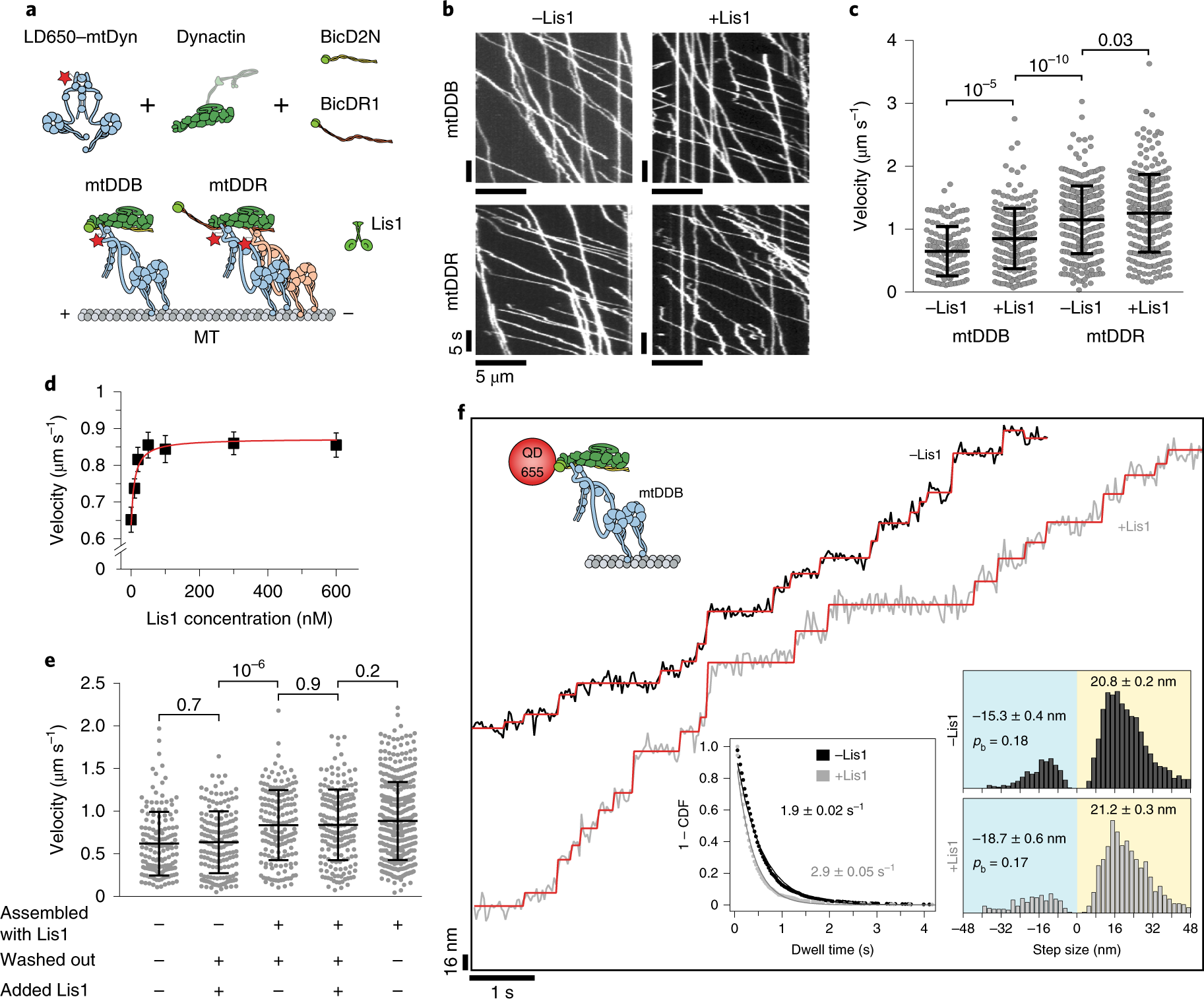
Lis1 activates dynein motility by modulating its pairing with dynactin
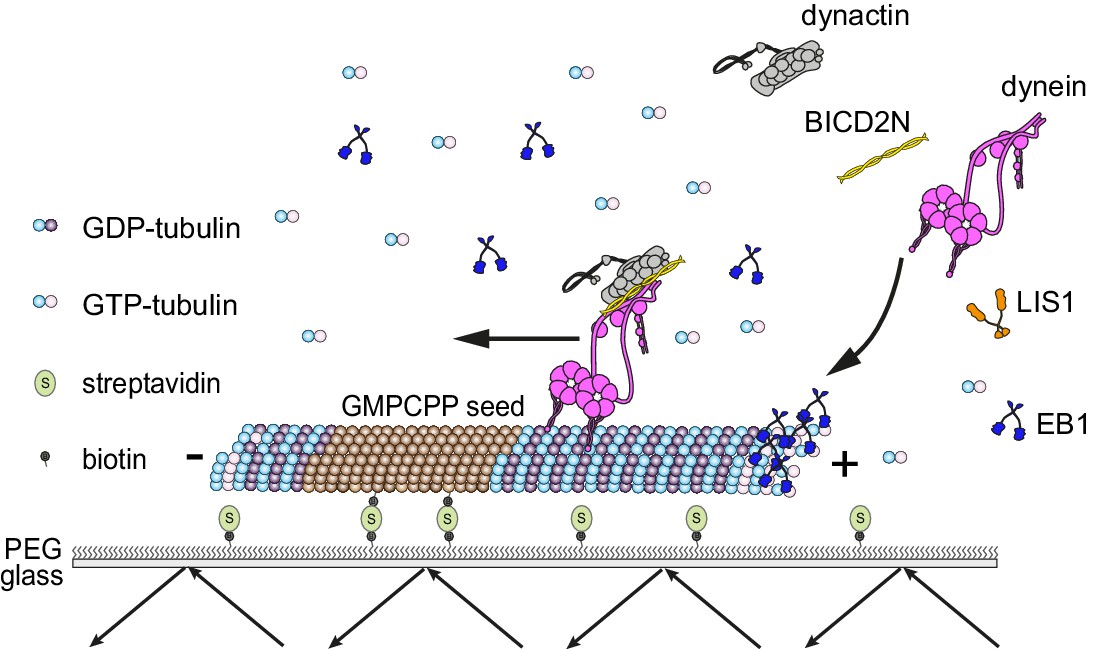
Lissencephaly-1 is a context-dependent regulator of the human dynein complex
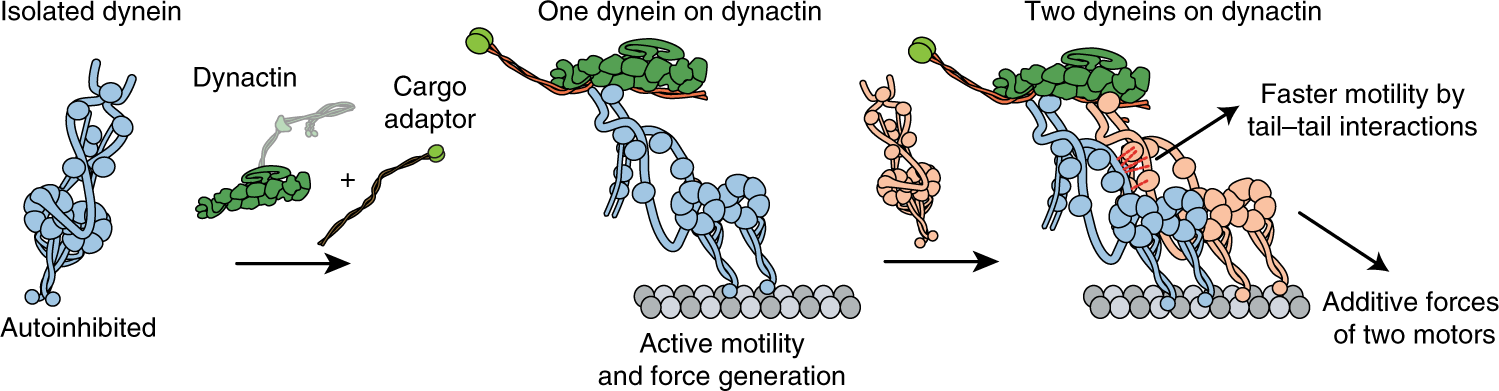
Cargo adaptors regulate stepping and force generation of mammalian dynein– dynactin
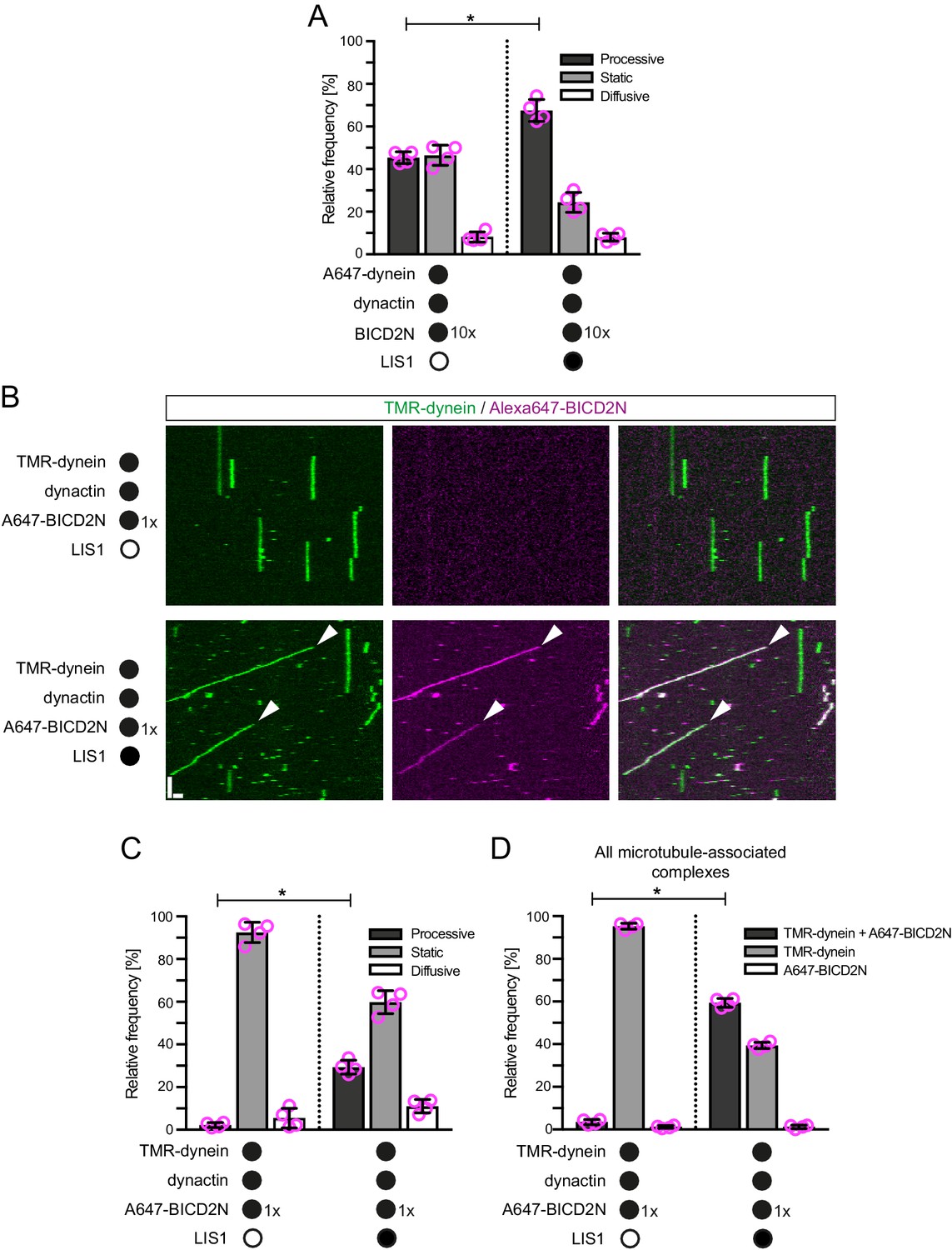
Lissencephaly-1 is a context-dependent regulator of the human dynein complex

Regulation of the processivity and intracellular localization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae dynein by dynactin
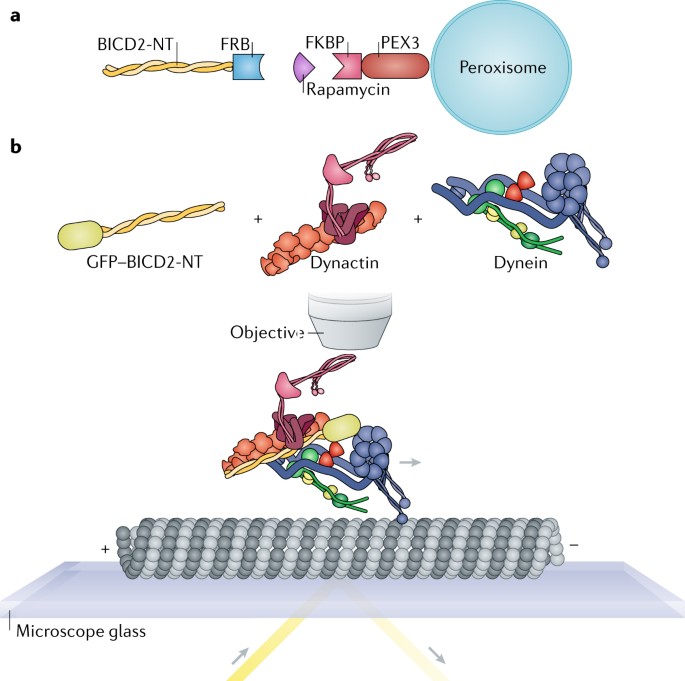
The cytoplasmic dynein transport machinery and its many cargoes

Load‐dependent detachment kinetics plays a key role in bidirectional cargo transport by kinesin and dynein - Ohashi - 2019 - Traffic - Wiley Online Library

Role of Dynactin in the Intracellular Localization and Activation of Cytoplasmic Dynein

Frontiers Sailing to and Docking at the Immune Synapse: Role of Tubulin Dynamics and Molecular Motors

The cytoplasmic dynein transport machinery and its many cargoes

Dynactin functions as both a dynamic tether and brake during dynein-driven motility

On and off controls within dynein–dynactin on native cargoes
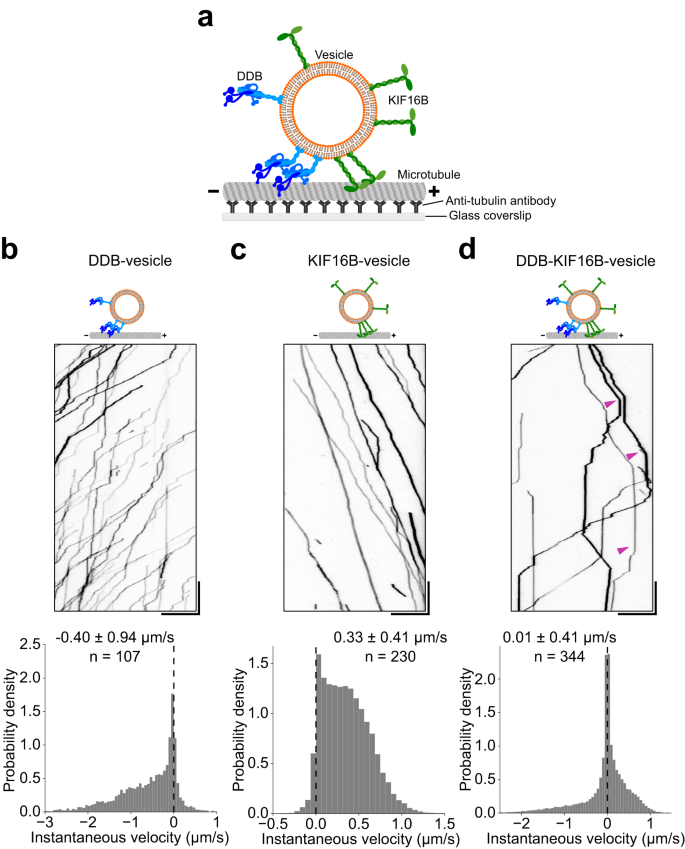
Vesicles driven by dynein and kinesin exhibit directional reversals without regulators