Correction for Weimer et al., UNC-13 and UNC-10/Rim Localize Synaptic Vesicles to Specific Membrane Domains

Functional Roles of UNC-13/Munc13 and UNC-18/Munc18 in Neurotransmission
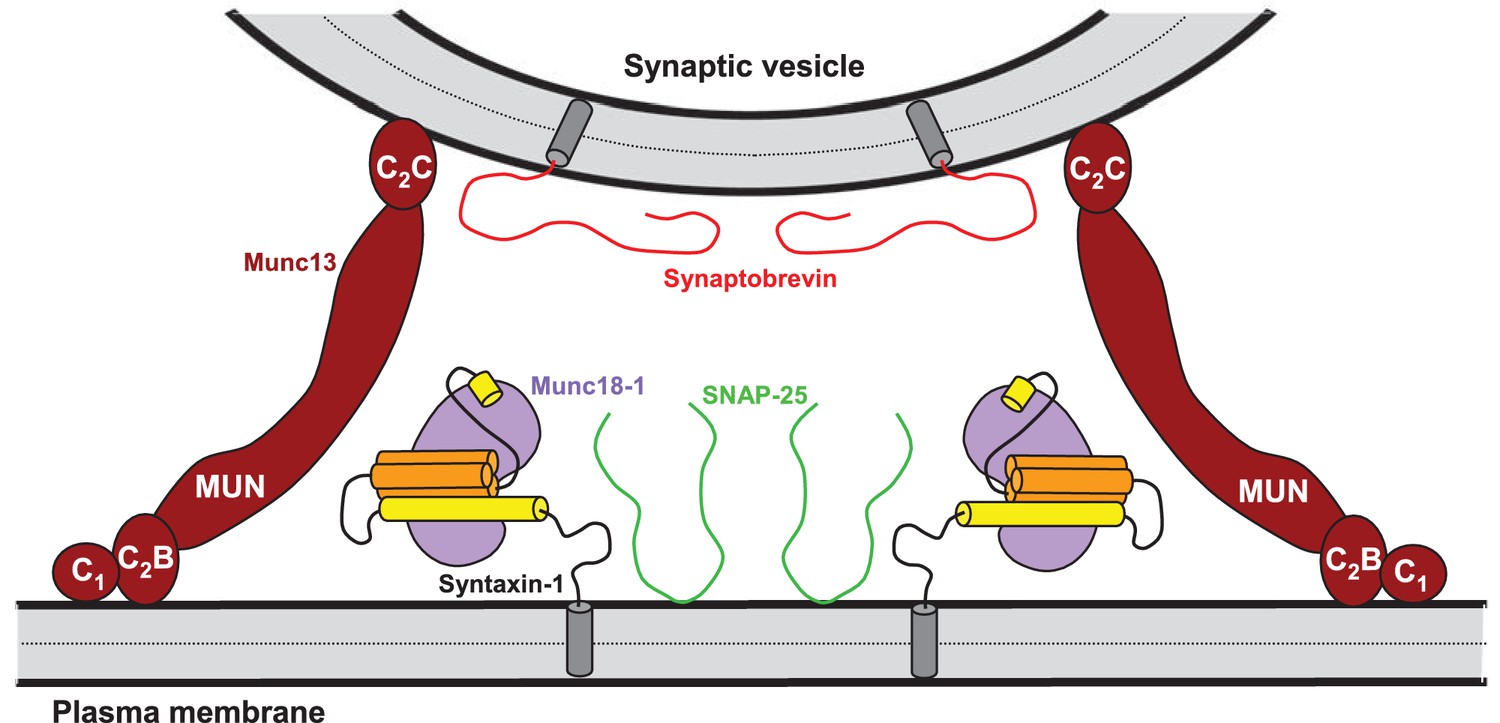
Functional synergy between the Munc13 C-terminal C1 and C2 domains
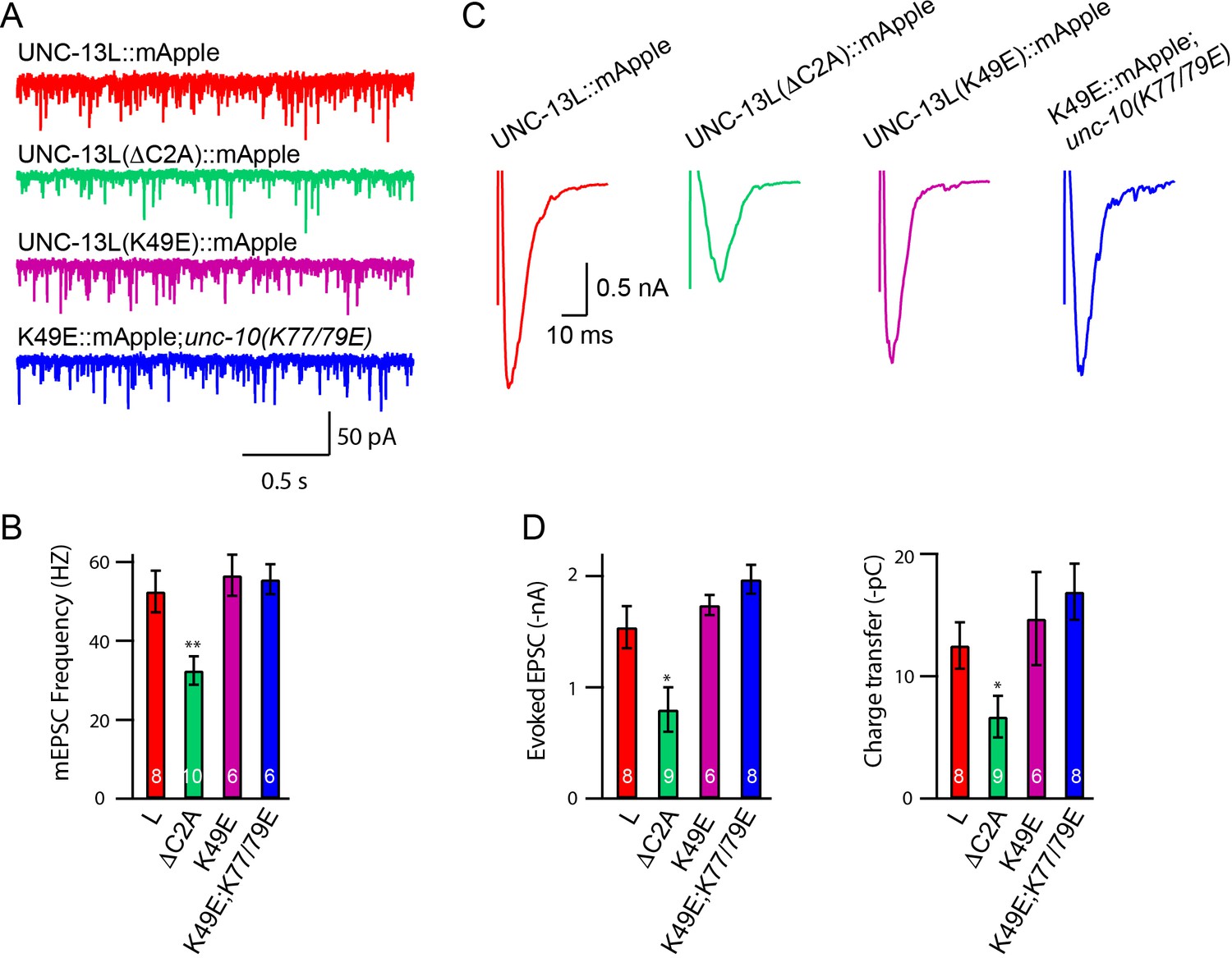
Heterodimerization of UNC-13/RIM regulates synaptic vesicle release probability but not priming in C. elegans
Heterodimerization of UNC-13/RIM regulates synaptic vesicle release probability but not priming in C. elegans

The M domain in UNC-13 regulates the probability of neurotransmitter release - ScienceDirect

PDF) The M domain in UNC-13 regulates the probability of neurotransmitter release

RIM-BP2 primes synaptic vesicles via recruitment of Munc13-1 at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses

A Hyperactive Form of unc-13 Enhances Ca2+ Sensitivity and Synaptic Vesicle Release Probability in C. elegans - ScienceDirect

The presynaptic machinery at the synapse of C. elegans
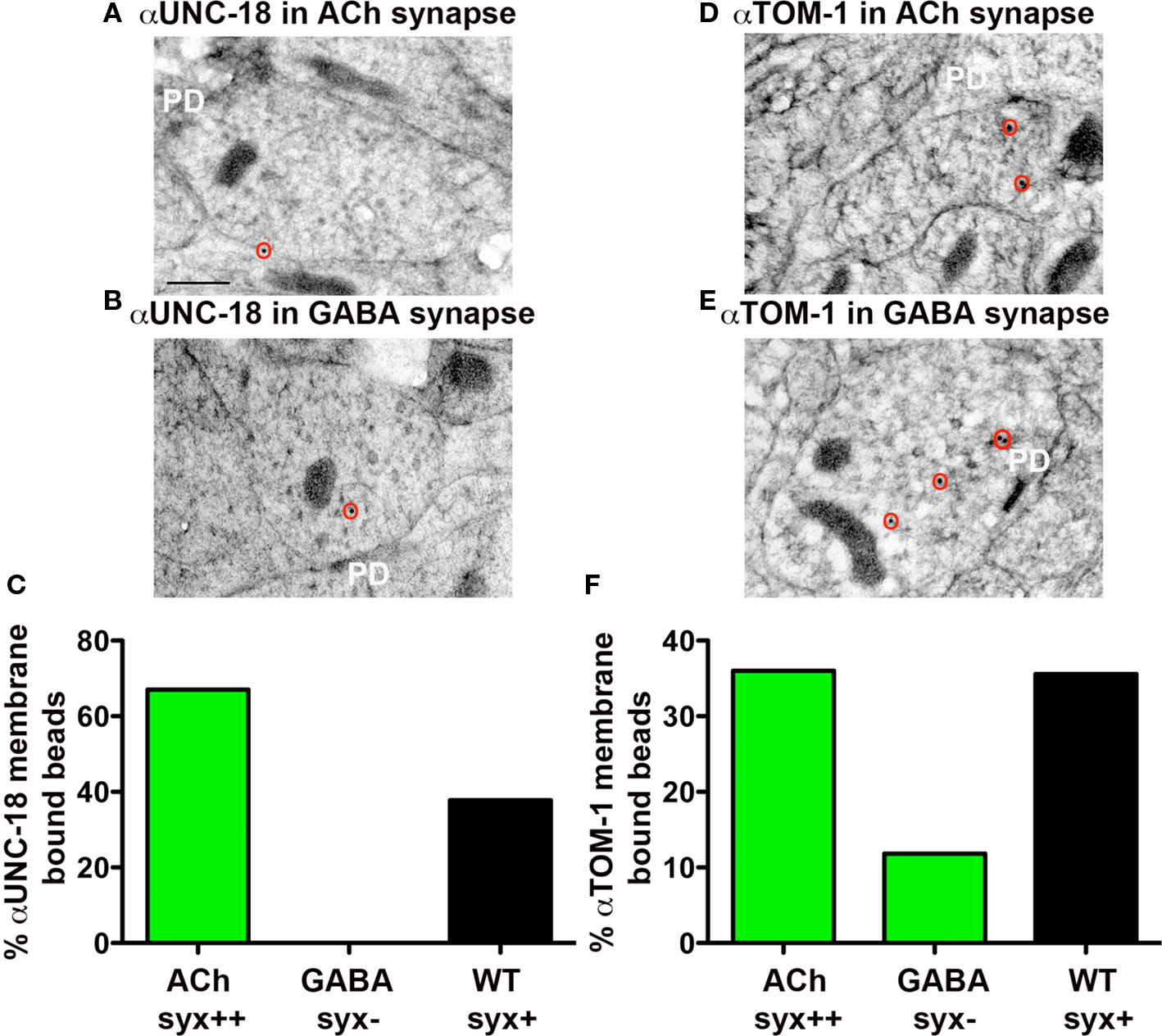
Frontiers Differential Regulation of Synaptic Vesicle Tethering and Docking by UNC-18 and TOM-1

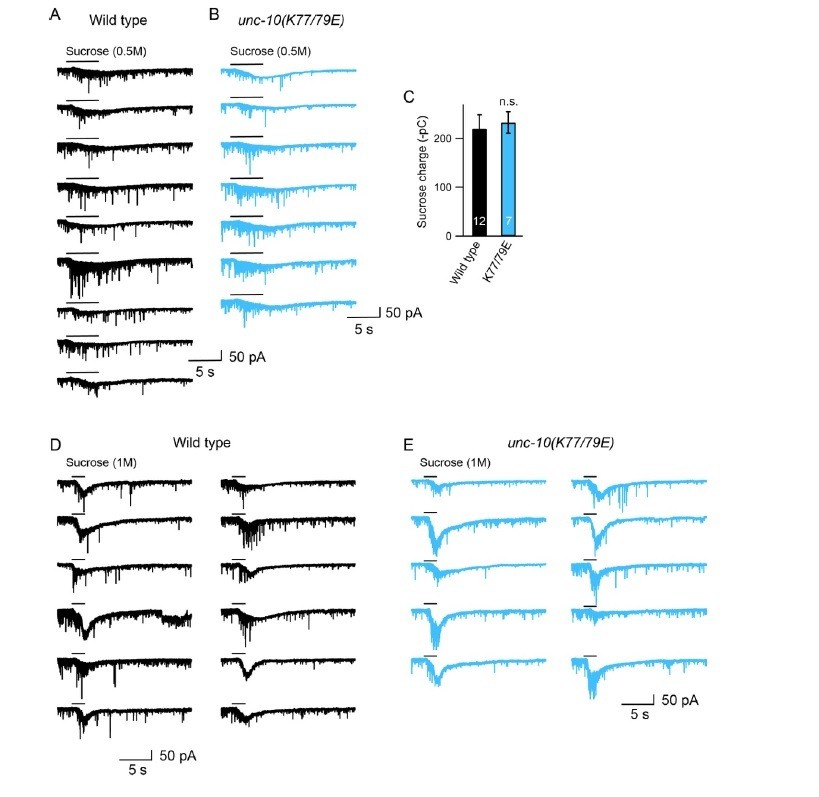
Tonic release is reduced by disrupting C2A/RIM heterodimerization in
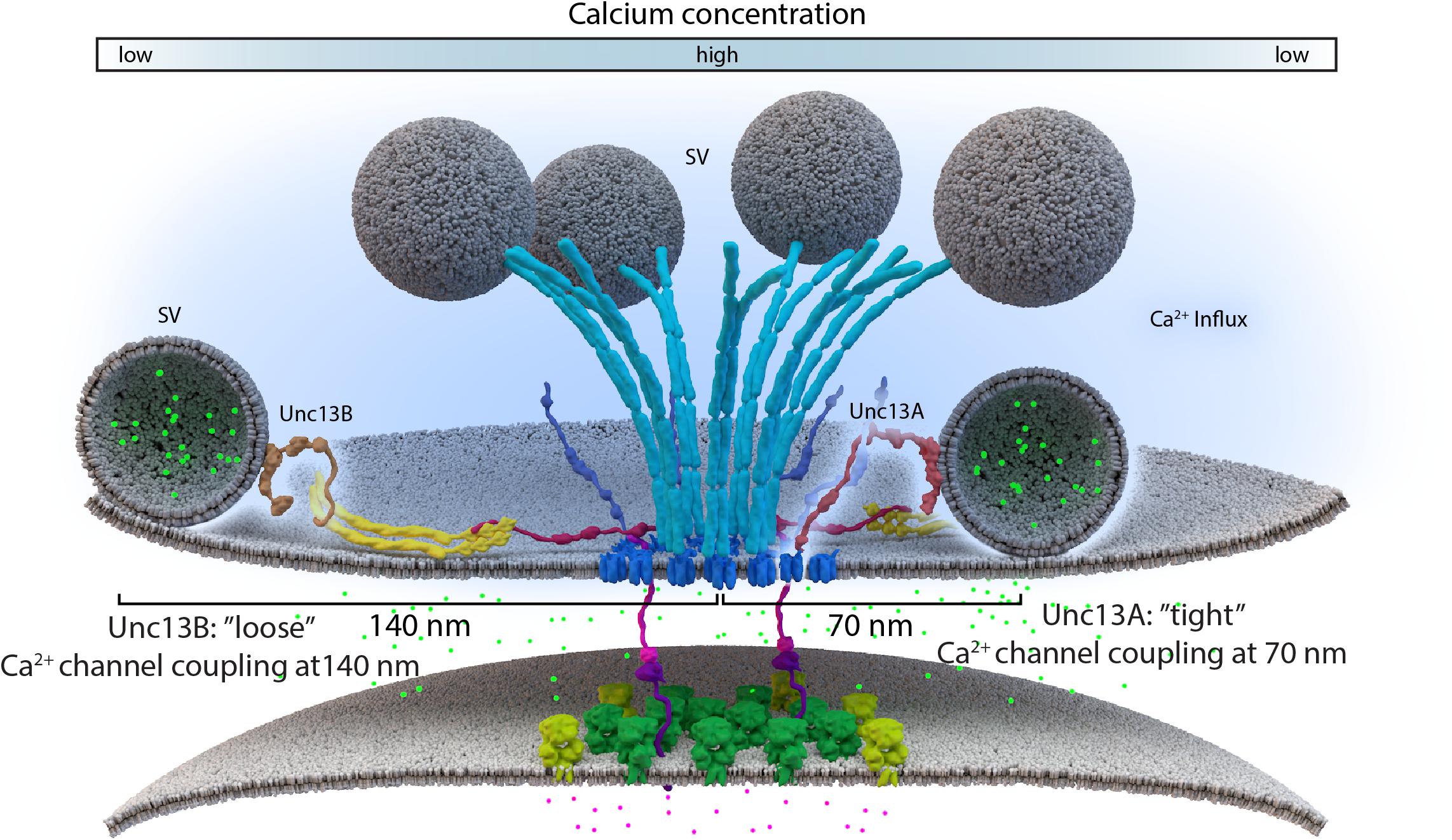
Frontiers Coupling the Structural and Functional Assembly of Synaptic Release Sites

Transcriptional Control of Parallel-Acting Pathways That Remove Specific Presynaptic Proteins in Remodeling Neurons

A unique C2 domain at the C terminus of Munc13 promotes synaptic vesicle priming
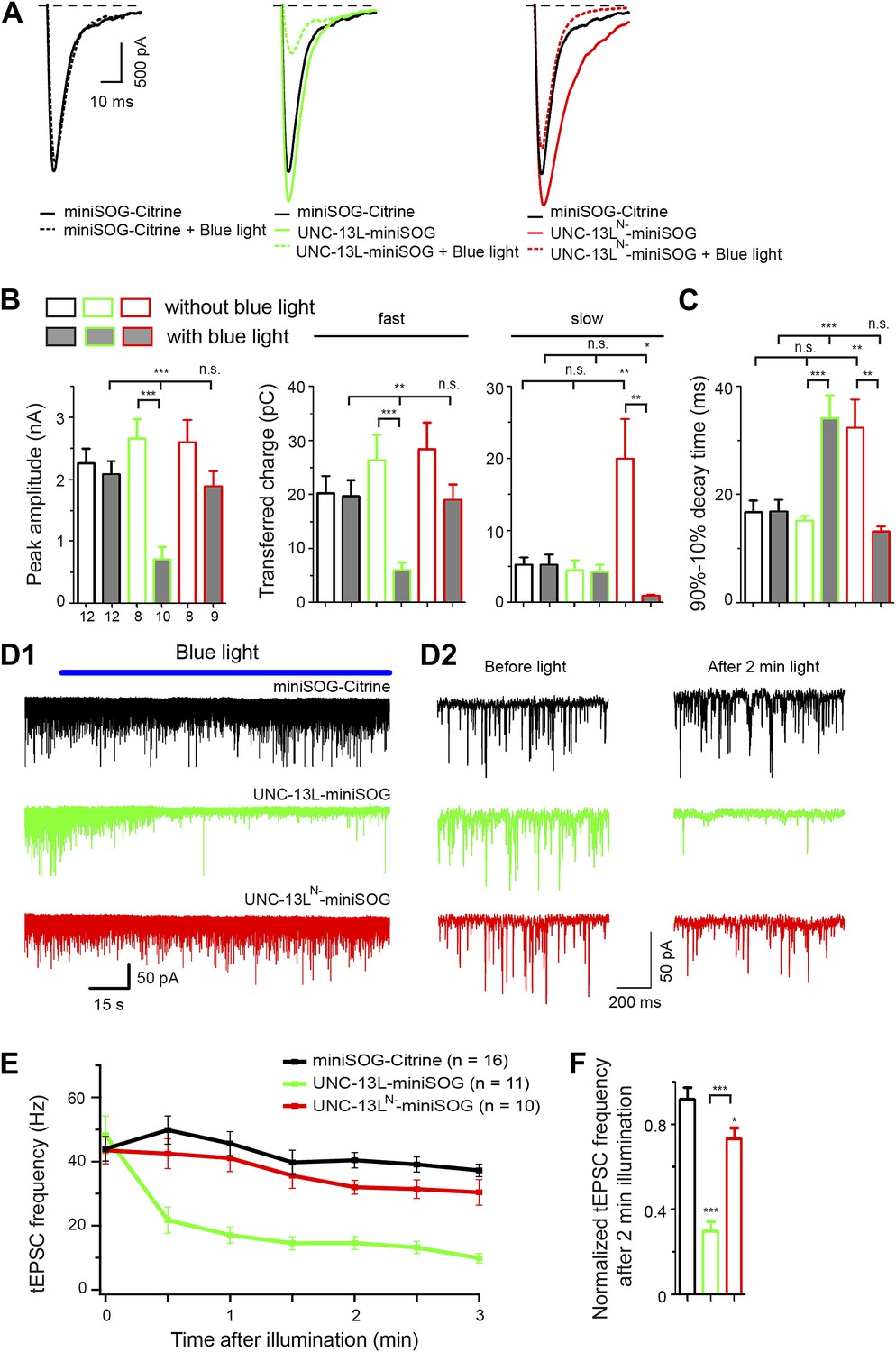
Position of UNC-13 in the active zone regulates synaptic vesicle release probability and release kinetics