CLA nitration by mitochondria, activated RAW 264.7 macrophages, MPO
Download scientific diagram | CLA nitration by mitochondria, activated RAW 264.7 macrophages, MPO, and ONOO ؊ . a, mitochondria (2 mg) were incubated in the presence of NO 2 Ϫ (0.25–1.0 m M ) and supplemented with various fatty acids (1 M ). Lipids were extracted, and NO 2 -FA was quantified by HPLC-MS/MS using [ 13 C 18 ]NO 2 -LA as internal standard. Results represent the mean Ϯ S.D. ( n ϭ 3), * indicates significantly different ( p Ͻ 0.05) from control without fatty acid addition. b, NO 2 -CLA formation from endogenous CLA and the concomitant CLA consumption was quantified by HPLC-MS/MS in mitochondria (2 mg) incubated with NO 2 Ϫ (1 m M ) at pH 6 ( n ϭ 3). c, chromatogram showing forma- from publication: Conjugated Linoleic Acid Is a Preferential Substrate for Fatty Acid Nitration | The oxidation and nitration of unsaturated fatty acids by oxides of nitrogen yield electrophilic derivatives that can modulate protein function via post-translational protein modifications. The biological mechanisms accounting for fatty acid nitration and the specific | Conjugated Linoleic Acid, Fatty Acids and Nitrate | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
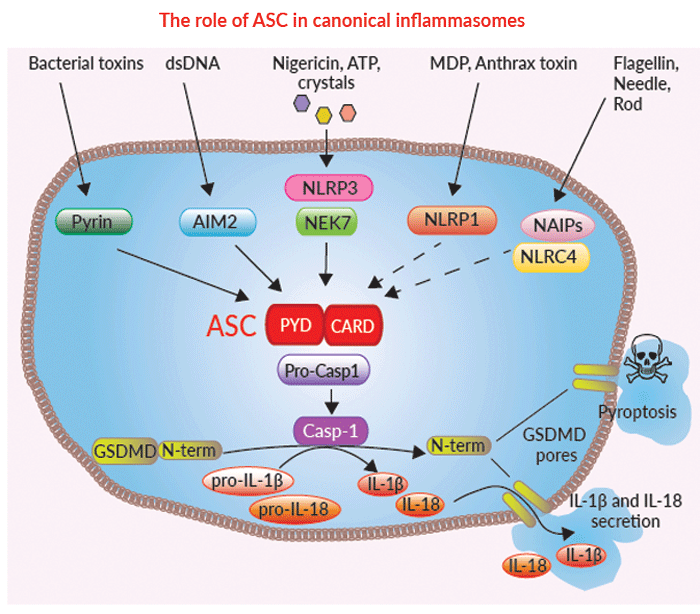
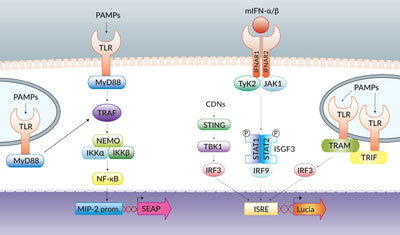
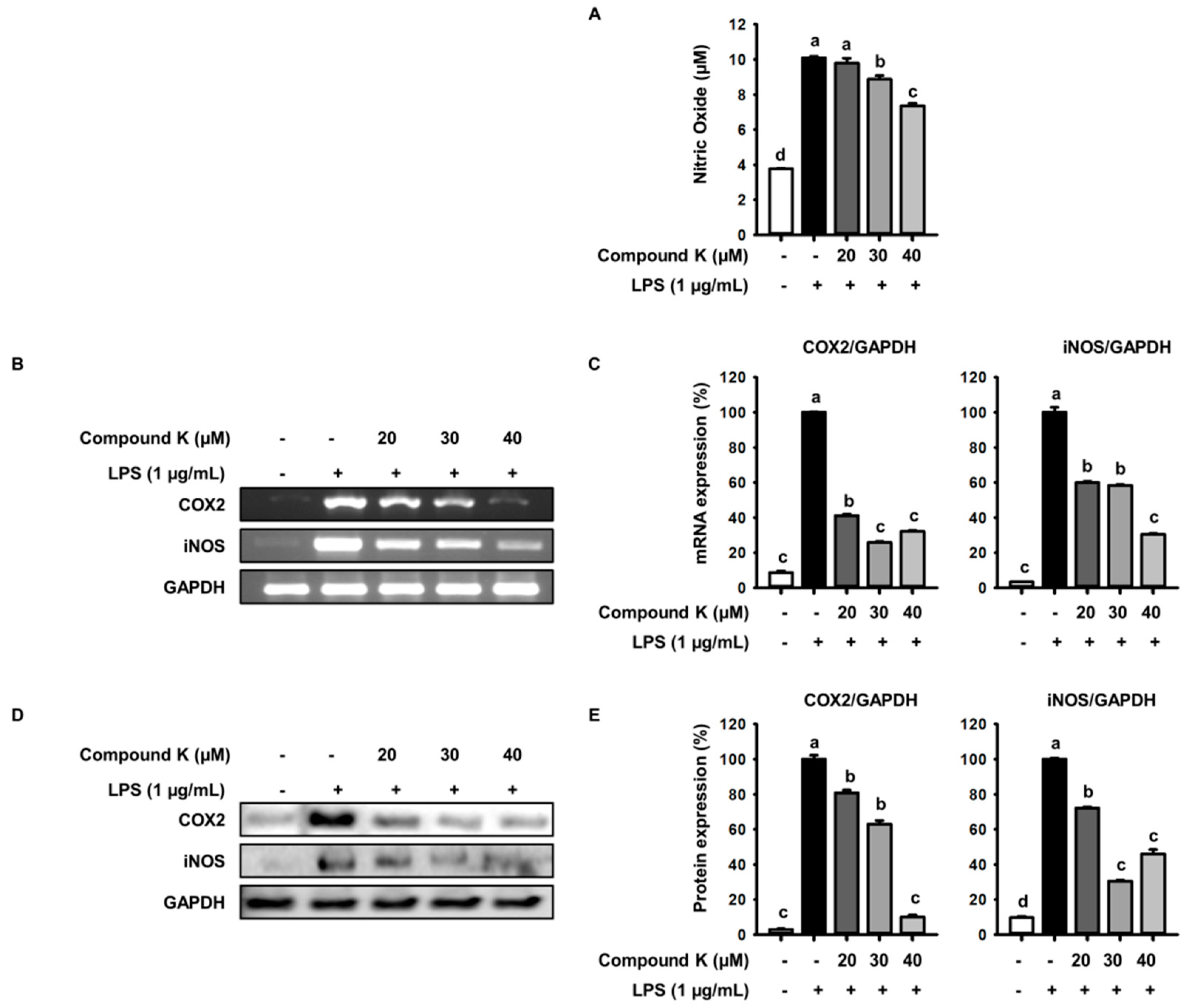
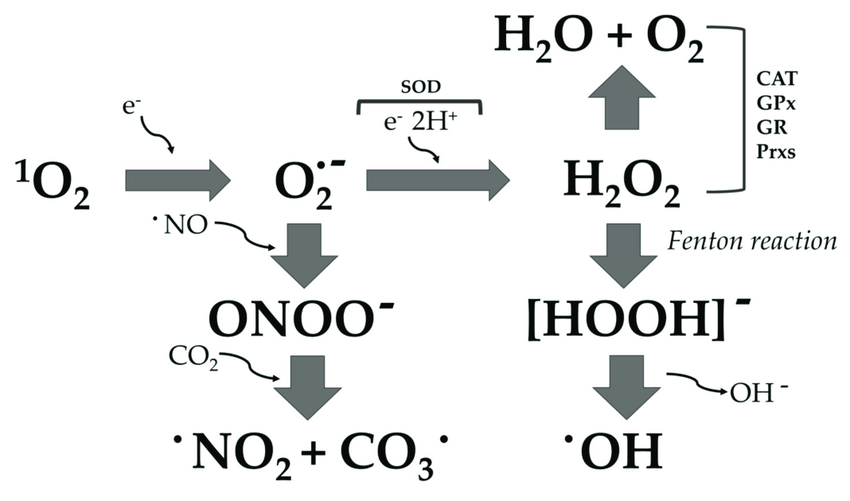
Anti‑inflammatory effects of Fritillaria thunbergii Morphological transformation in RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with Redox Signaling by Reactive Electrophiles and Oxidants Discovery of bioactive nitrated lipids and nitro-lipid-protein ASC expressing RAW cells, Inflammasome test macrophages Andrographolide acts as an anti-inflammatory agent in LPS Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in RAW 264.7 cells by Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation RAW-Dual™ cells IFN & NF-κB reporter macrophages Nitric Oxide-induced Apoptosis in RAW 264.7 Macrophages Is Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text