
Peroxynitrite Inhibits Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel Activity in Smooth Muscle of Human Coronary Arterioles
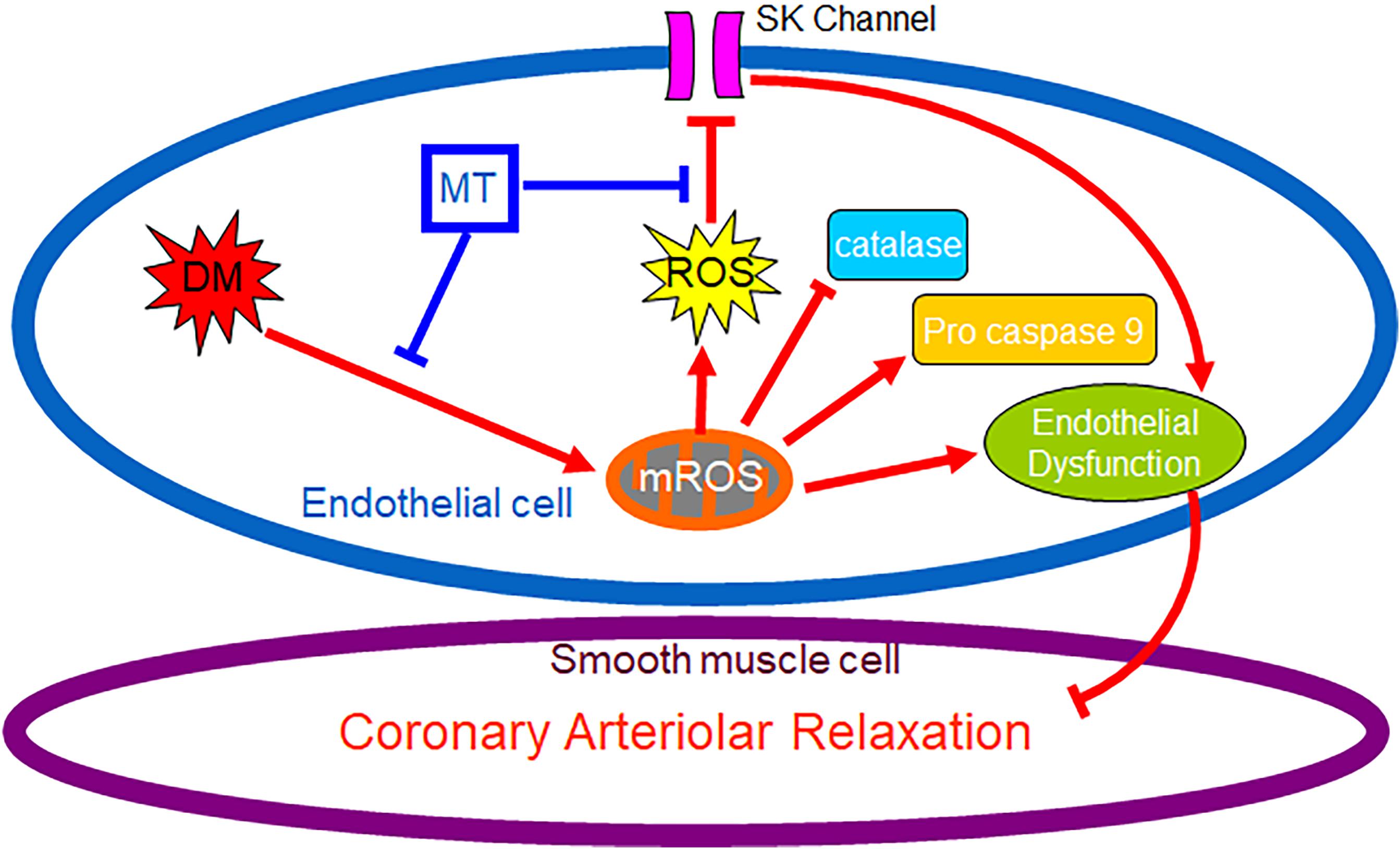
Frontiers Chronic Inhibition of mROS Protects Against Coronary Endothelial Dysfunction in Mice With Diabetes
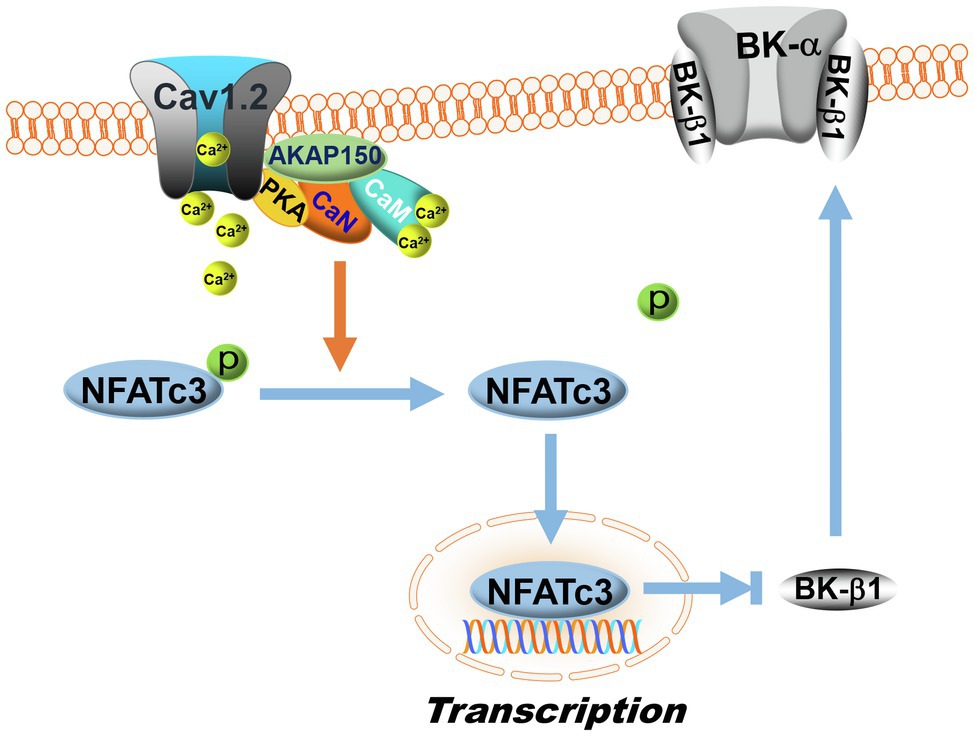
Frontiers Coronary Large Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus
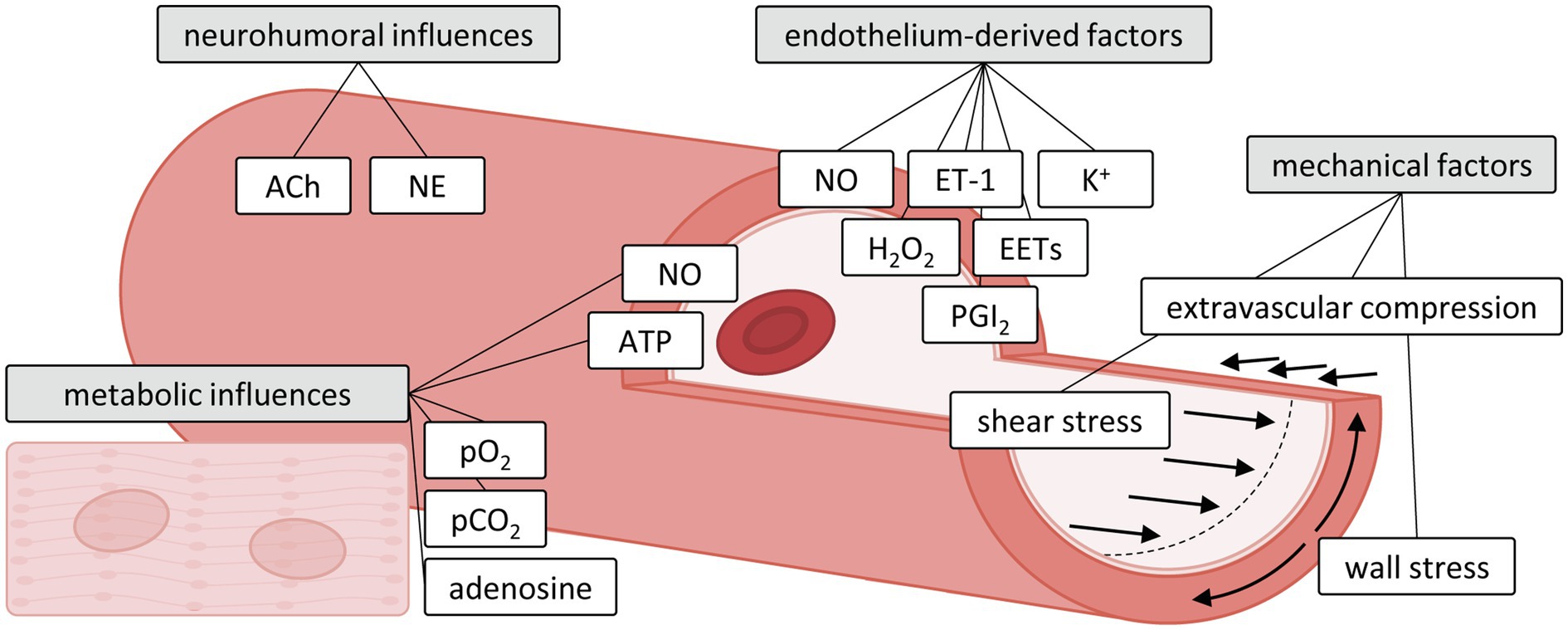
Frontiers Mechanobiology of Microvascular Function and Structure in Health and Disease: Focus on the Coronary Circulation

Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Inhibition of Human Large Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels by High Glucose

The Large-Conductance, Calcium-Activated Potassium Channel: A Big Key Regulator of Cell Physiology. - Abstract - Europe PMC
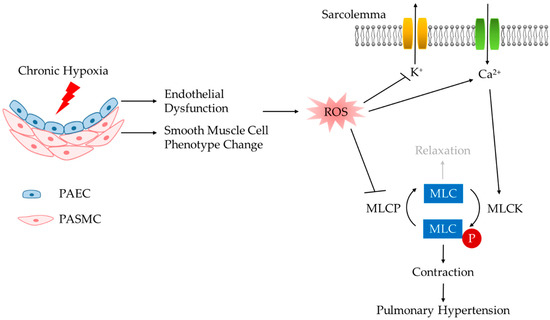
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

Peroxynitrite reversibly inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in rat cerebral artery smooth muscle cells
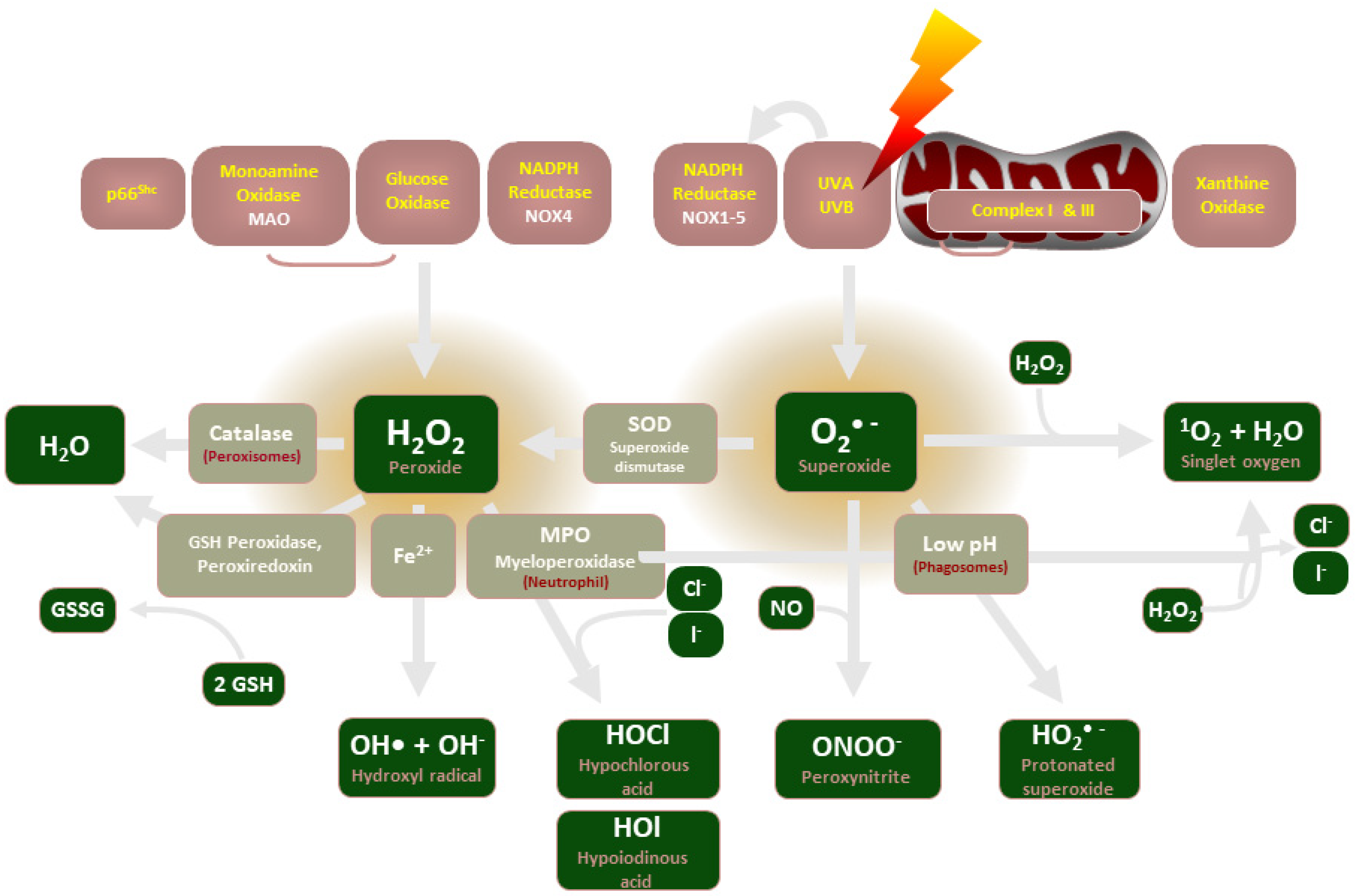
Biomolecules, Free Full-Text

Peroxynitrite reversibly inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in rat cerebral artery smooth muscle cells

Peroxynitrous acid-modified extracellular matrix alters gene and protein expression in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells and induces a pro-inflammatory phenotype - ScienceDirect

Modulation of the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway in cardiac contraction and relaxation: Potential role in heart failure treatment - ScienceDirect

Involvement of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) in mPRα (PAQR7)-mediated progesterone induction of vascular smooth muscle relaxation

H2O2-Induced Dilation in Human Coronary Arterioles: Role of Protein Kinase G Dimerization and Large-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel Activation

Mitochondrial mechanisms by which gasotransmitters (H2S, NO and CO) protect cardiovascular system against hypoxia







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Screen-Shot-2019-06-11-at-12.50.54-PM-0ab612f158d143d4a7b67c09616465d1.png)

